Kutoma Wakunuma IF we are to build a greener, fairer and more equal society in the wake of COVID-19, it is time for rich countries to end the practice of dumping plastic waste in developing countries.
This not only harms the environment but disproportionately affects the women and girls who clear it up.
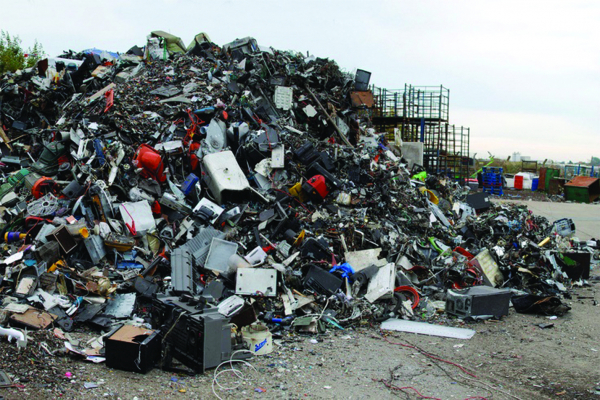
The problem was made worse for many developing countries when China announced its refusal to accept other countries’ plastic waste in 2018. The result has been an increase in plastic waste exports to Africa, much of which are proving hard to recycle and are ending up in rivers and oceans.
On top of this, the pandemic is generating ever-increasing amounts of plastic waste, especially single-use items like medical gloves and disposable masks.
In some areas of Africa — where around 411 million face masks are discarded everyday — lack of plastic waste management infrastructure and weak regulations around dumping waste mean the situation is only getting worse.
Now, countries like Ghana, Uganda, Tanzania, Ethiopia, Senegal and Kenya are finding themselves flooded with plastic waste.
This is overwhelmingly affecting poor, socially marginalised people, and women in particular.
Unfair trade
- Chamisa under fire over US$120K donation
- Mavhunga puts DeMbare into Chibuku quarterfinals
- Pension funds bet on Cabora Bassa oilfields
- Councils defy govt fire tender directive
Keep Reading
Although plastic waste can be seen as a trade between developed and developing countries, which allows the latter to be paid in exchange for dealing with waste, this trade isn’t an equal one.
Developing countries are likely to accept plastic waste from developed countries because it is a potential source of income for their population living below the poverty line.
It’s projected that 27 million to 40 million people in sub-Saharan Africa will fall into extreme poverty during 2021. It’s no wonder that such regions see plastic waste as a lucrative opportunity which can contribute to easing poverty.
People pick waste from a landfill
The plastic waste trade is rooted in inequality.
However, the amounts paid to waste pickers — usually women — by private waste collecting companies barely make a dent in pickers’ financial needs. Payments of less than 4 cents a kilogramme for collecting plastic bottles for recycling are normal.
And that waste sometimes ends up burned, rather than being recycled. In 2020, 40% of UK’s plastic waste was sent to Turkey, where instead of being recycled some of it was illegally dumped and burned. Research in 2019 suggested that the equivalent of a double-decker bus full of plastic ends up dumped or burned every second.
Health and security
Many plastics contain toxic chemicals that can enter the environment if products are discarded or burnt. This includes substances that have been linked to miscarriages and cancer.
Picking plastic waste not only doesn’t pay well, it also comes at a price in terms of health and security. Dumped waste can contain hazardous materials like broken glass and syringes carrying infectious illnesses. Plus, women are often forced to collect plastic from the outskirts of cities: places likely to have higher rates of crime.
Most, however, don’t have a choice: they must risk their safety to make a living and provide for their families, due to widespread lack of education for women and girls.
Across Africa, 3 million more girls than boys between six and 11 years of age will not get the opportunity to attend school.
The impacts of this ripple into their future, making it far less likely for women to find well-paying jobs and forcing many to resort to low-paid, dangerous work.
Many poorer women in African countries also reside in informal settlements, where waste easily accumulates due to poor rubbish collection services.
Accumulating plastic can damage water drainage systems, resulting in flourishing colonies of dangerous bacteria. For example, Zambia has experienced several cholera outbreaks due to poor drainage worsened in part by plastic-clogged systems.
Justice
It’s imperative to find ways of improving women’s situations in developing countries if we are to realise a truly greener, fairer and more equal world.
Some next steps to consider — if such a world is to become a reality — developing countries should create more stringent legislation against plastic dumping, increase women’s education and involve more women in decision-making processes around how to deal with plastic waste.
What’s more, creating social incentives for reducing plastic waste — for example, by paying pickers more — is key in societies where social status is attached to those who can afford bottled water and removed from those who pick up their litter.
Community-based awareness programmes promoting the importance of plastic waste management — run via community clubs, social platforms like Facebook and Instagram, or local radio stations — could help achieve this.
If picking plastic waste became better paid, this kind of cultural shift would not only help to empower women pickers economically but might be able to eliminate stigma attached to picking. With the resulting influx of formalised training courses, policies to keep pickers safe and opportunities for pickers to speak out about the issues attached to their work, many others will hopefully be attracted to picking litter to help keep their local environments clean and safe.
Kutoma Wakunuma is an associate professor of information systems at De Montfort University, Leicester, England